A Breakthrough
in Immunotherapy
We’re revolutionizing immunotherapy by harnessing the power of granzyme B to transform cancer and autoimmune disease treatments.[I]Investigational status. CSB-321 and CSB-421 are investigational product candidates. They have not been approved by the U.S. FDA or any other regulatory authority for safety or efficacy. Any references to potential clinical utility reflect development goals only. Our PET imaging radiodiagnostic can provide early mechanistic insights[II]Biomarker / imaging purpose. Statements referring to “early mechanistic insights” or “real-time activity” describe investigational imaging endpoints that assess signals consistent with immune engagement. These measures are not, by themselves, diagnostic of clinical benefit, and are not intended to replace standard-of-care assessments. into a drug’s effectiveness, and our breakthrough preclinical radioimmunotherapy has shown a 100% response rate in rescuing immunotherapy non-responses in animal models.[III]Preclinical limitation. Results such as “100% response rate” refer to non-clinical (animal) models under controlled study conditions and may not predict outcomes in humans. Preclinical data are subject to important limitations, including species and model differences, dosing, and study design.
Granzyme B — The Immunotherapy Biomarker Your Pipeline Can’t Afford to Miss
When cancer wages war, our bodies send T and NK immune cells to fight the battle. They find tumors and release granzyme B, a protein that acts like “bullets” entering tumors and triggering apoptosis,[IV]Biology depiction. Descriptions of granzyme B “bullets” and apoptosis are simplified explanations of complex immune mechanisms. Imaging detects signals consistent with immune activation; it does not directly visualize apoptosis or confirm cell death in patients. a signal that instructs the tumor to self-destruct. We harness the power of those granzyme B bullets, the key to our groundbreaking radiodiagnostic and radiotherapeutic immunotherapy solutions.[I]Investigational status. CSB-321 and CSB-421 are investigational product candidates. They have not been approved by the U.S. FDA or any other regulatory authority for safety or efficacy. Any references to potential clinical utility reflect development goals only.
Raise the Bar—Direct, Real-Time Assessment That Your Therapy Works
Our first-in-class granzyme B radiodiagnostic PET scan[V]“First-in-class” qualifier. “First-in-class” reflects CytoSite Bio’s good-faith assessment of publicly available information regarding granzyme B–targeted radiopharmaceutical imaging as of the page’s publication date and may not capture all global research activities. represents a paradigm shift in clinical trial assessment. Unlike traditional metabolic or anatomical scans, our investigational CSB-321 PET tracer measures the immune system’s real-time activity[II]Biomarker / imaging purpose. Statements referring to “early mechanistic insights” or “real-time activity” describe investigational imaging endpoints that assess signals consistent with immune engagement. These measures are not, by themselves, diagnostic of clinical benefit, and are not intended to replace standard-of-care assessments. at all tumor sites,[VI]Site-level signal, not whole-patient outcome. CSB-321 PET aims to visualize signal at lesion sites consistent with immune engagement. Signal presence, absence, or change at a given site may not reflect overall patient response or long-term outcomes. providing an early mechanistic assessment of a drug within days.[VII]Timing claims. References to “within days” or “as early as 14 days” reflect observations in early studies with specific protocols. Actual timing, thresholds, and interpretability vary by indication, therapy, and study design. Early functional evidence of treatment engagement—showing which tumors are active and how they change over time—could enable swift go/no-go decisions, accelerated clinical timelines, and de-risking of pipelines[VIII]Development / forward-looking statements. Statements about enabling go/no-go decisions, accelerating timelines, “de-risking,” or resource optimization are forward-looking and based on preliminary findings. Actual results depend on future studies, regulatory feedback, and other factors. See “Forward-Looking Statements” below. by focusing resources only on effective therapies.
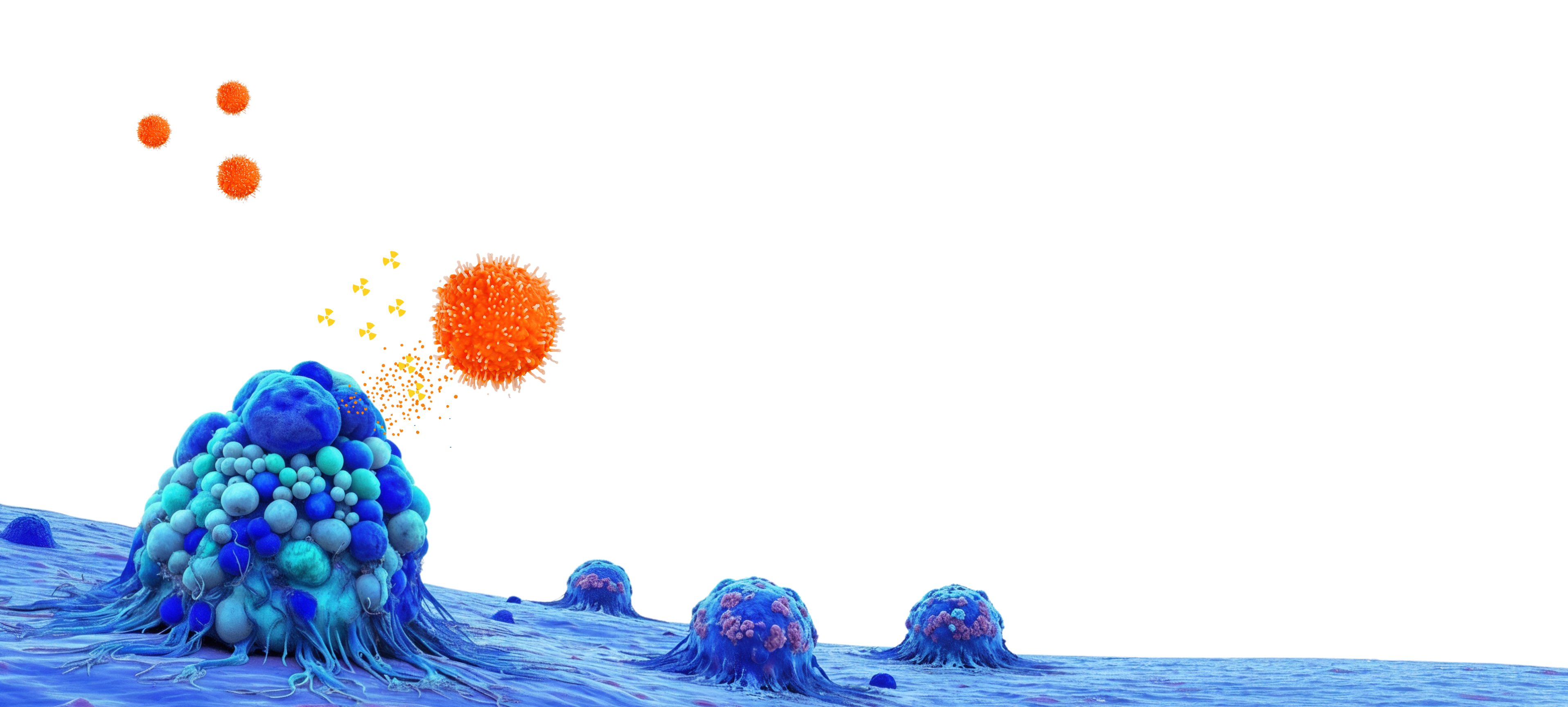
Pioneering Granzyme B Radiotherapeutics — A New Paradigm of Immunotherapy
Our CSB-421 preclinical radioimmunotherapy is designed to bind to extracellular granzyme B at tumor hotspots and use immunostimulatory radiation to amplify immune attack. In study models, our data showed 100% complete responses while sparing healthy tissue—offering a targeted option for dynamic, metastatic, or therapy-resistant tumors.
Clinical Results That Drive Confidence
Radiodiagnostic Data
CSB-321 is our granzyme B–guided PET radiodiagnostic, developed and evaluated over multiple clinical studies,[IX]Clinical-study context. Mentions of “multiple clinical studies,” specific indications, or datasets refer to early clinical research conducted under study-specific protocols and inclusion/exclusion criteria. Study populations, endpoints, and analytical methods vary and may limit generalizability. that visualizes immune attack as it happens. Across multiple indications, our results thus far show >95% sensitivity and specificity for predicting immunotherapy response (see figure captions for N, thresholds, and CIs).[X]Sensitivity/specificity qualifiers. Performance metrics (e.g., “>95% sensitivity and specificity”) reflect results from specific study cohorts and analyses (with defined thresholds and confidence intervals). Metrics may differ across indications, timepoints, and analysis plans. Readers should consult figure captions and Methods for N, thresholds, and CIs. These findings are preliminary and require confirmation in larger, prospective studies. Lesion-level signals have been detected as early as 14 days after the start of immunotherapy.[VII]Timing claims. References to “within days” or “as early as 14 days” reflect observations in early studies with specific protocols. Actual timing, thresholds, and interpretability vary by indication, therapy, and study design. Explore five data sets—melanoma, NSCLC, colitis, inflammatory lung disease, and combination therapy.[IX]Clinical-study context. Mentions of “multiple clinical studies,” specific indications, or datasets refer to early clinical research conducted under study-specific protocols and inclusion/exclusion criteria. Study populations, endpoints, and analytical methods vary and may limit generalizability.
Radiotherapeutic Data
CSB-421 is our preclinical radioimmunotherapy designed to target granzyme B where T and NK cells are actively engaging tumors[XI]Mechanism under investigation. The proposed mechanism of CSB-421 (binding to extracellular granzyme B and delivering immunostimulatory radiation) is based on preclinical data and has not been established in humans. Dose, scheduling, and combinatorial approaches remain subject to evaluation. and release focused radiation to enhance the immune response. In a murine model, the regimen achieved 100% complete response vs. control;[III]Preclinical limitation. Results such as “100% response rate” refer to non-clinical (animal) models under controlled study conditions and may not predict outcomes in humans. Preclinical data are subject to important limitations, including species and model differences, dosing, and study design. click below for dosing, N, timing, and Methods.[XII]Methods and definitions. Preclinical “complete response,” dosing, timing, N, controls, and statistical methods are defined in the referenced study materials. Different models or definitions can materially change outcomes.
Breakthroughs the World is Watching
-
I
Investigational status. CSB-321 and CSB-421 are investigational product candidates. They have not been approved by the U.S. FDA or any other regulatory authority for safety or efficacy. Any references to potential clinical utility reflect development goals only.
-
II
Biomarker / imaging purpose. Statements referring to “early mechanistic insights” or “real-time activity” describe investigational imaging endpoints that assess signals consistent with immune engagement. These measures are not, by themselves, diagnostic of clinical benefit, and are not intended to replace standard-of-care assessments.
-
III
Preclinical limitation. Results such as “100% response rate” refer to non-clinical (animal) models under controlled study conditions and may not predict outcomes in humans. Preclinical data are subject to important limitations, including species and model differences, dosing, and study design.
-
IV
Biology depiction. Descriptions of granzyme B “bullets” and apoptosis are simplified explanations of complex immune mechanisms. Imaging detects signals consistent with immune activation; it does not directly visualize apoptosis or confirm cell death in patients.
-
V
“First-in-class” qualifier. “First-in-class” reflects CytoSite Bio’s good-faith assessment of publicly available information regarding granzyme B–targeted radiopharmaceutical imaging as of the page’s publication date and may not capture all global research activities.
-
VI
Site-level signal, not whole-patient outcome. CSB-321 PET aims to visualize signal at lesion sites consistent with immune engagement. Signal presence, absence, or change at a given site may not reflect overall patient response or long-term outcomes.
-
VII
Timing claims. References to “within days” or “as early as 14 days” reflect observations in early studies with specific protocols. Actual timing, thresholds, and interpretability vary by indication, therapy, and study design.
-
VIII
Development / forward-looking statements. Statements about enabling go/no-go decisions, accelerating timelines, “de-risking,” or resource optimization are forward-looking and based on preliminary findings. Actual results depend on future studies, regulatory feedback, and other factors. See “Forward-Looking Statements” below.
-
IX
Clinical-study context. Mentions of “multiple clinical studies,” specific indications, or datasets refer to early clinical research conducted under study-specific protocols and inclusion/exclusion criteria. Study populations, endpoints, and analytical methods vary and may limit generalizability.
-
X
Sensitivity/specificity qualifiers. Performance metrics (e.g., “>95% sensitivity and specificity”) reflect results from specific study cohorts and analyses (with defined thresholds and confidence intervals). Metrics may differ across indications, timepoints, and analysis plans. Readers should consult figure captions and Methods for N, thresholds, and CIs. These findings are preliminary and require confirmation in larger, prospective studies.
-
XI
Mechanism under investigation. The proposed mechanism of CSB-421 (binding to extracellular granzyme B and delivering immunostimulatory radiation) is based on preclinical data and has not been established in humans. Dose, scheduling, and combinatorial approaches remain subject to evaluation.
-
XII
Methods and definitions. Preclinical “complete response,” dosing, timing, N, controls, and statistical methods are defined in the referenced study materials. Different models or definitions can materially change outcomes.
Be a Part of Our Success